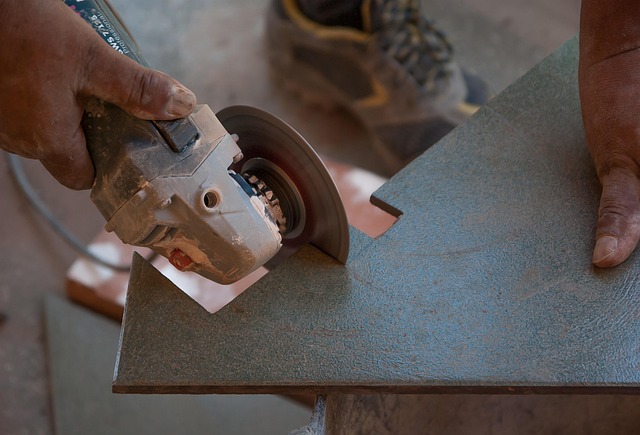
Glue Laminated Beams (GLT) and Engineered Wood Beams offer enhanced structural advantages for construction. GLT uses advanced glues to bond wood veneers, providing exceptional strength, stability, and warping resistance compared to traditional lumber. They support heavier loads and longer spans, simplifying design. Engineered Wood Beams employ fusion techniques with adhesives to improve dimensional integrity, fire resistance, and load-bearing capacity over mechanical fastenings. Both have unique benefits; engineers and architects choose based on specific project needs, focusing on strength, durability, cost, design versatility, and longevity.
When considering structural elements for your building project, understanding the nuances between Glue Laminated Beams and Engineered Wood Beams is crucial. This article offers a comprehensive guide, breaking down the key properties, benefits, and considerations of each type. We’ll help you navigate the choices by comparing their unique advantages in strength, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Whether you’re a professional or DIY enthusiast, this insight will empower your decision between Glue Laminated Beam vs. Engineered Wood Beam for your next project.
- Understanding Glue Laminated Beams: Key Properties and Benefits
- Engineered Wood Beams: Features, Advantages, and Considerations
- Comparison: Choosing Between Glue Laminated and Engineered Wood Beams
Understanding Glue Laminated Beams: Key Properties and Benefits

Glue Laminated Beams, often referred to as Glued Laminated Timber (GLT), represent a cutting-edge advancement in structural engineering, offering unique properties that set them apart from traditional Engineered Wood Beams. The key lies in their manufacturing process: advanced glues are used to bond multiple layers of wood veneers, creating robust beams with exceptional strength and dimensional stability. This method significantly enhances the natural resistance of timber against warping, splitting, and cracking, ensuring structural integrity over time.
In a Glue Laminated Beam vs. Engineered Wood Beam comparison, GLT emerges as a superior choice for various reasons. Firstly, the laminating process allows for larger beam sizes without sacrificing strength, enabling more versatile design options in architecture. Secondly, glue lamination offers advantages over traditional wooden joists by providing a stronger, more consistent bond. This leads to improved structural performance and longevity, especially in heavy-load applications. Moreover, GLT’s environmental benefits are noteworthy; its production involves less waste and energy compared to conventional timber processing, making it an eco-friendly alternative. For those seeking a reliable and sustainable building solution, give us a call at (607) 369-9341 to explore how Glue Laminated Beams can transform your construction project.
Engineered Wood Beams: Features, Advantages, and Considerations
Engineered Wood Beams: Features, Advantages, and Considerations
Engineered wood beams are modern structural components crafted by fusing multiple layers of wood veneers with high-performance adhesives, creating a versatile and robust alternative to traditional solid lumber. This innovative process enhances strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to warping or cracking, making engineered wood beams ideal for various construction needs. The primary advantage lies in their ability to withstand heavy loads and span longer distances compared to conventional wooden joists, thus simplifying beam placement and design flexibility in architectural plans.
When comparing Glue Laminated Beams vs. Engineered Wood, the former refers to a specific type of engineered wood beam where layers of wood are glued together under high pressure, creating a strong and uniform structural element. This method significantly improves the mechanical properties of timber. In contrast, traditional solid lumber joins rely on mechanical fastenings like nails or screws, which may not offer the same level of strength and durability as glue lamination. Advantages of glue laminating for beam construction include superior structural integrity, reduced warping, and enhanced fire resistance, making it a preferred choice in modern building practices.
Comparison: Choosing Between Glue Laminated and Engineered Wood Beams

When comparing Glue Laminated Beams vs. Engineered Wood Beams, several key factors come into play, each highlighting unique advantages and considerations for structural integrity in construction projects. At its core, the debate revolves around understanding the distinct characteristics of each option.
Glue Laminated Beams vs Engineered Wood: Structural Comparison reveals significant differences in their manufacturing processes. Glue laminated beams are created by applying adhesive to multiple layers of wood, pressing them together, and curing them to form a strong, unified structure. In contrast, engineered wood beams, often made from fast-growing species, involve sophisticated engineering techniques to enhance their strength and stability. These include gluing, pressing, and sometimes adding internal connectors for added rigidity. The result is a high-performance material that combines the advantages of both individual wood elements and a fully integrated beam.
Considerations such as strength and durability, particularly in bearing heavy loads (e.g., how do engineered wood beams withstand heavy loads?, beam strength: comparison of glue laminating vs mechanical fastening), are crucial for structural engineers and architects. Advantages of glue laminating for beam construction offer enhanced tensile and compressive strength, making glued laminated timber a compelling choice for applications demanding exceptional structural integrity, like in modern green architecture. Interested parties should also explore cost analysis: glue laminated vs engineered wood beams, versatility of engineered wood in architectural designs, and longevity of glue laminated beams in building projects to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. For more insights, visit us at 18 Clifton St, Unadilla, NY 13849.
When selecting structural components for your building project, understanding the nuances between glue laminated beams and engineered wood beams is key. Both offer strength and versatility, but each has unique properties. Glue laminated beams excel in load-bearing capacity and durability, while engineered wood beams provide cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits. By considering factors like structural requirements, budget, and sustainability goals, you can make an informed decision between these two innovative options, ensuring the best choice for your specific needs. Whether opting for a Glue Laminated Beam or Engineered Wood Beam, both are reliable game-changers in modern construction.